Exchanging Tokens
If you want to do various things in the NEAR ecosystem, you can’t just have NEAR tokens and do everything with it. Some NFTs can be bought only with a specific token, some DAOs require a specific token to vote, or maybe you just don’t want to worry about the price of NEAR and want to use a stablecoin.
Since we’re covering the NEAR ecosystem, we’ll focus on DEXes (decentralized exchanges) that are available on NEAR, but there are other ways to exchange tokens, like centralized exchanges and OTC.
At the time of writing, the biggest DEX on NEAR is Ref Finance. To start using it, you have to connect your wallet and then you can start swapping tokens.
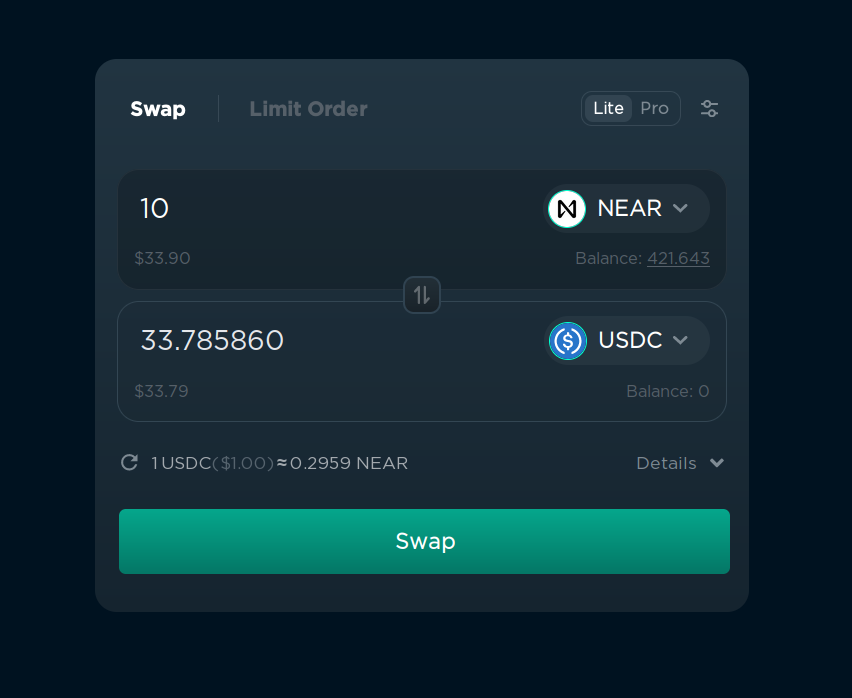
To convert one token into another, follow these steps:
- Choose the token you want to swap from on the right of the first input field (“NEAR” on the screenshot).
- Choose the token you want to swap to on the right of the second input field (“USDC” on the screenshot).
- Enter the amount of the tokens you want to swap.
- Click “Swap” and confirm the transaction in your wallet.
Yes, it’s that simple. But if you’re going to do it often, you should be aware of these things:
How prices work
The price of a token depends on how much people buy and sell the token. If a lot of people are buying a token, the price goes up, and if a lot of people are selling a token, the price goes down. If you want to know more about technical details and the formula, you can read about liquidity.
Price impact
If you’re buying or selling a lot of tokens at once, the price can change a lot, depending on the liquidity of the token. If the token has a low liquidity, the price can change by a lot, even if you’re swapping just $10. If the token has a high liquidity, the price will not change by much, even if you’re swapping $10,000 at once. This could potentially lead to a situation where you change the price by 10%, and your average buy price is 5% higher than the current price.
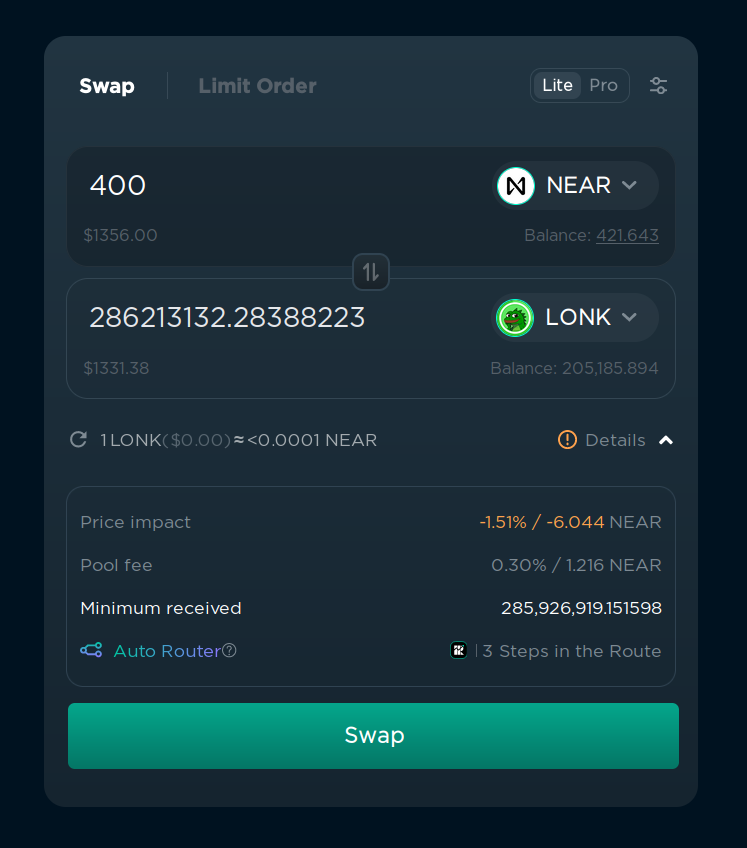
If the price will be changed by more than 1%, ref.finance will show you a warning about the price impact and an estimated loss under “Details” in the bottom right corner. You can ignore it if you’re sure that you want to swap the tokens, but be aware that you’ll get a bad price.
Slippage
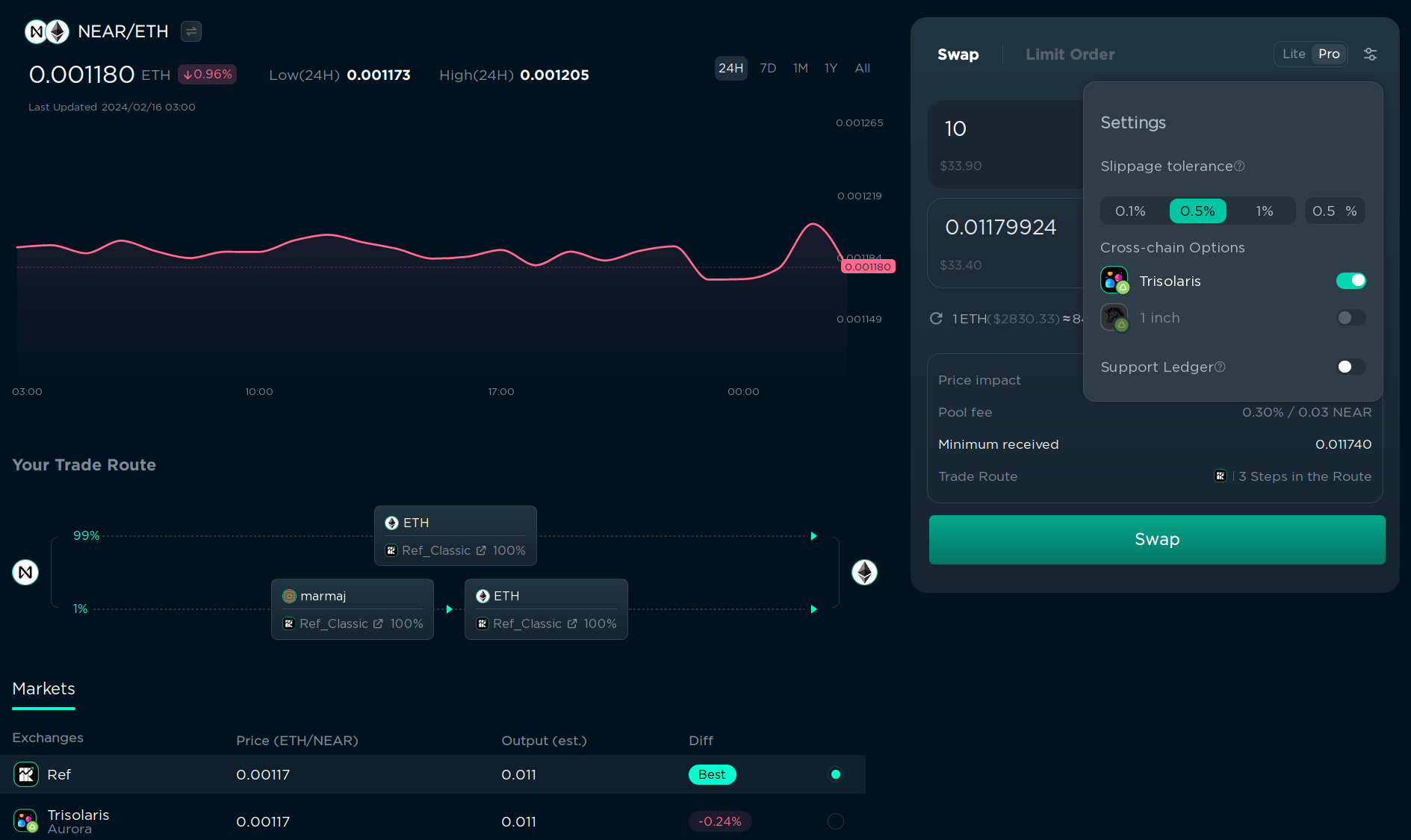
Slippage is the difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is executed. It can happen when the market is volatile and the price of the token changes between the moment you click “Swap” and the moment the transaction is confirmed. If the slippage is too high, the transaction will fail. You can set the maximum slippage in the settings in the top right corner.
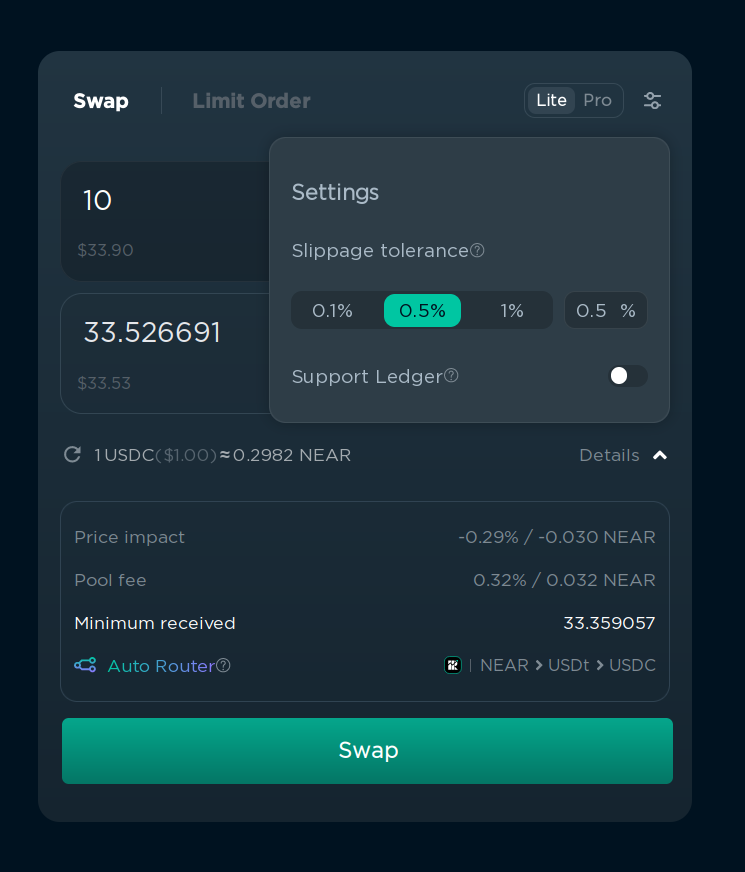
This is done to prevent you from losing money when the price changed too much between the moment you clicked “Swap” and the moment the transaction was confirmed. For example, if you want to swap 1 NEAR for 3.37 USDC, and the price of NEAR changes from $3.37 to $3.10, the transaction will fail, because the price has changed by a lot. It also protects you from “sandwich attacks”, where someone can manipulate the price of the token by buying right before your transaction and selling after your transaction, so you buy for a higher price. These attacks are not common because they’re much harder to execute on NEAR, but it’s still better to set slippage to a reasonable value.
I recommend setting it to 0.1% for popular tokens, and 0.5% for less popular tokens, but if the swap constantly fails because of “slippage error”, you can increase it farther. If you’re trading a token that has transfer fees, you can also increase the slippage to cover the fee. You can see the amount you are guaranteed to receive under “Details”, and if the amount is less than you expect, the transaction will be reverted and you will get your tokens back.
If you want to buy a token just after the launch, you should set the slippage to 5-10% because the price can change a lot in a few seconds.
Routing
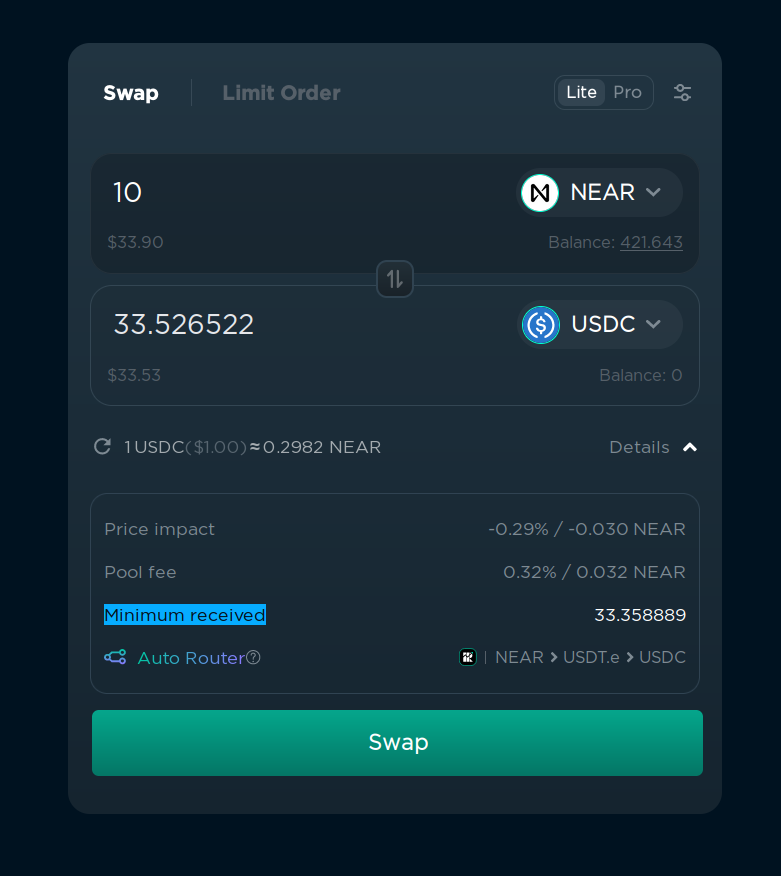
Ref.finance will try to get the best price possible by combining multiple tokens pairs. For example, sometimes instead of swapping NEAR -> UDSC, it will be better to swap NEAR -> ETH -> USDC. This is called “routing”. You can see the routing details if you enable “Pro” mode in the top right corner.
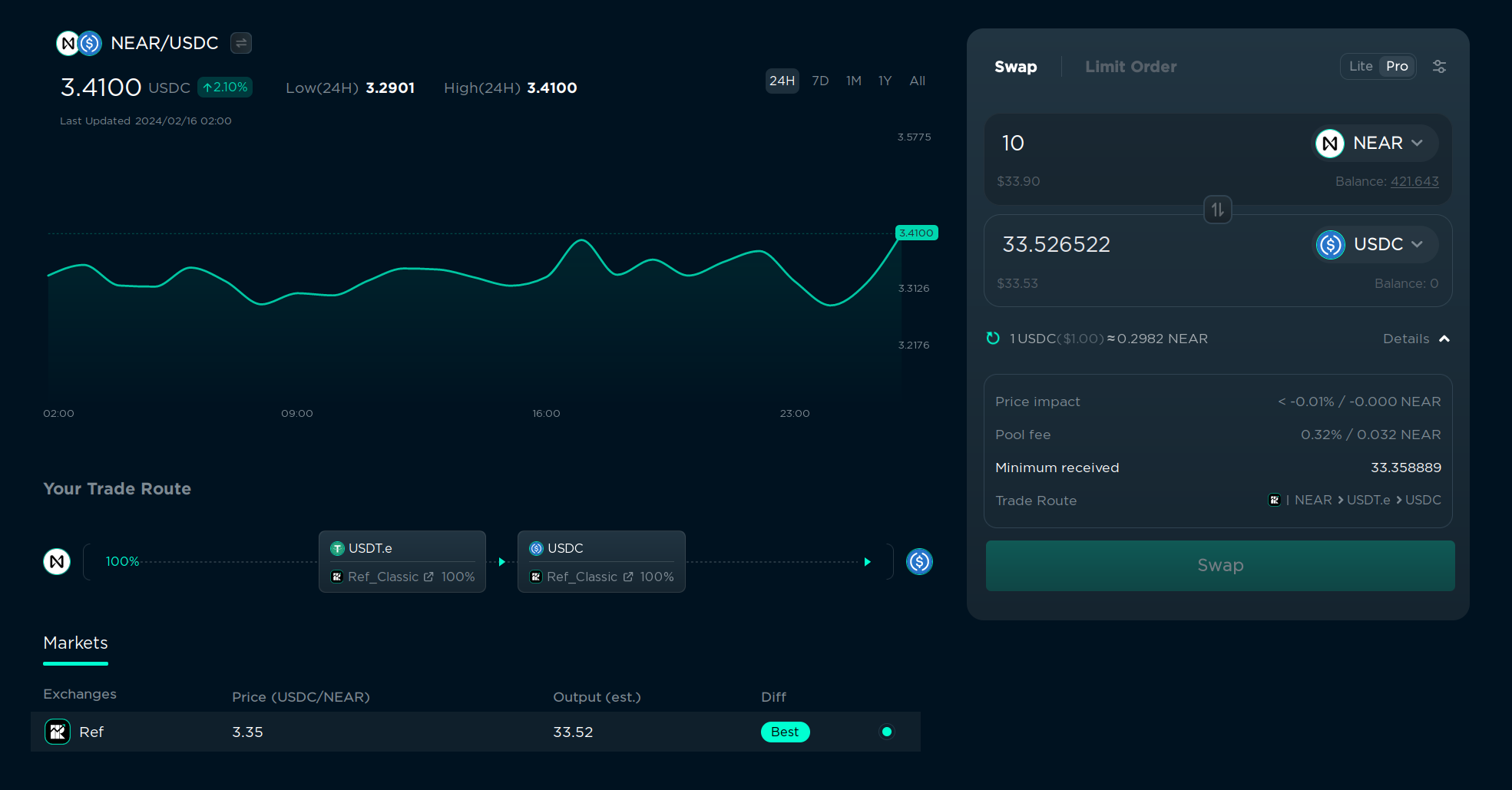
In this example, it will swap NEAR to USDT.e, and then USDT.e to USDC. It can also route using the transaction using different paths, for example, swap 14% directly to USDC, and 86% to USDT.e, and then swap USDT.e to USDC. This is done automatically, so you don’t have to worry about it, but it’s good to know that it’s happening.
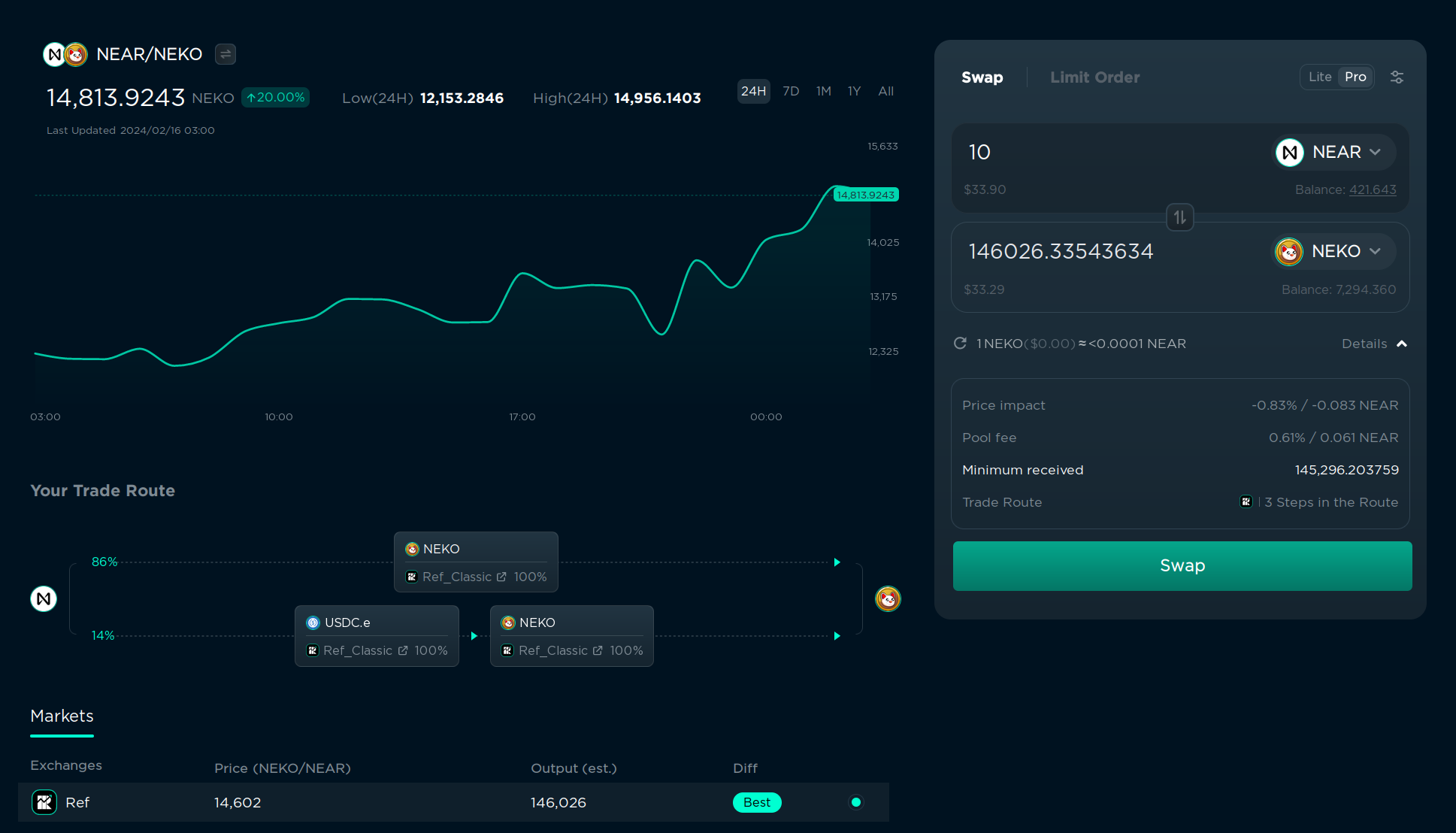
If you enabled Pro mode, you can also enable Trisolaris routing. Trisolaris is the most popular DEX on Aurora, and if the token is available on both NEAR and Aurora, it will try to find the best between both chains. This is also done automatically, but you can choose the route manually in the left bottom corner if you want.
Trading less popular tokens
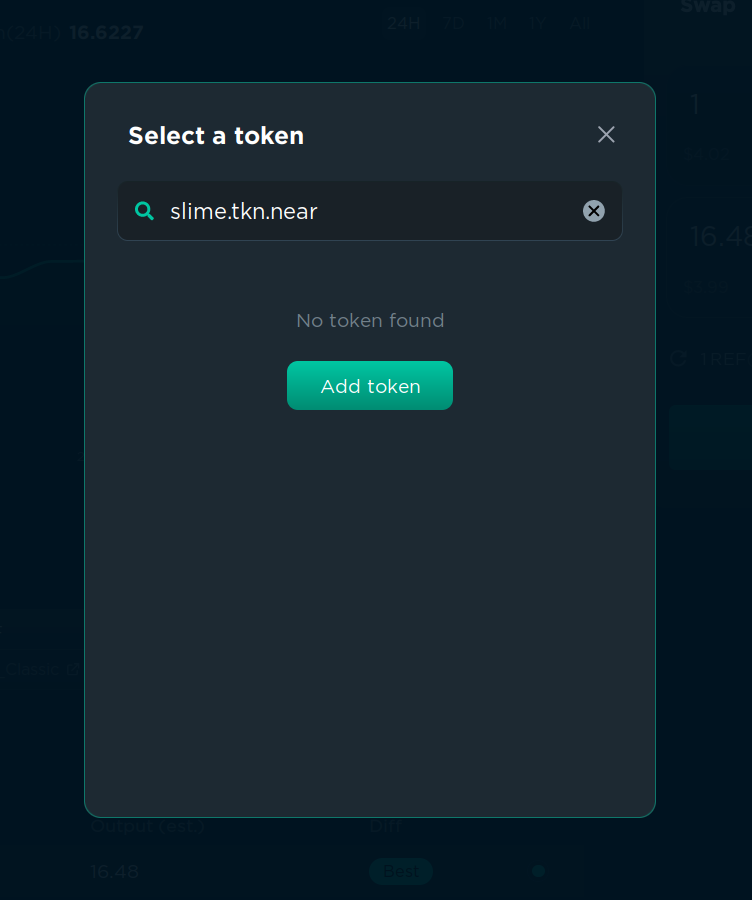
Not all tokens are available in “Select a token” menu, but if you have a token address (or contract address), you can enter it manually in the “Search name or paste address…” field. After that, click the “Add token” button and confirm the transaction. The transaction is needed to save the token in your list of tokens, and it will cost a small storage fee. After that, you will be able to find the token in the “Select a token” menu. As the project gains more recognition, Ref’s team might whitelist it so that this action is no longer necessary.
Limit orders
If you want to buy a token for a specific price, you can use a limit order. This will create a transaction that will be executed when the price of the token reaches the price you specified. This is useful if you want to buy a token, but you think that the price is too high right now, and you want to buy it only if the price goes down. You can toggle between “Swap” and “Limit Order” in the top left corner of the swap menu.
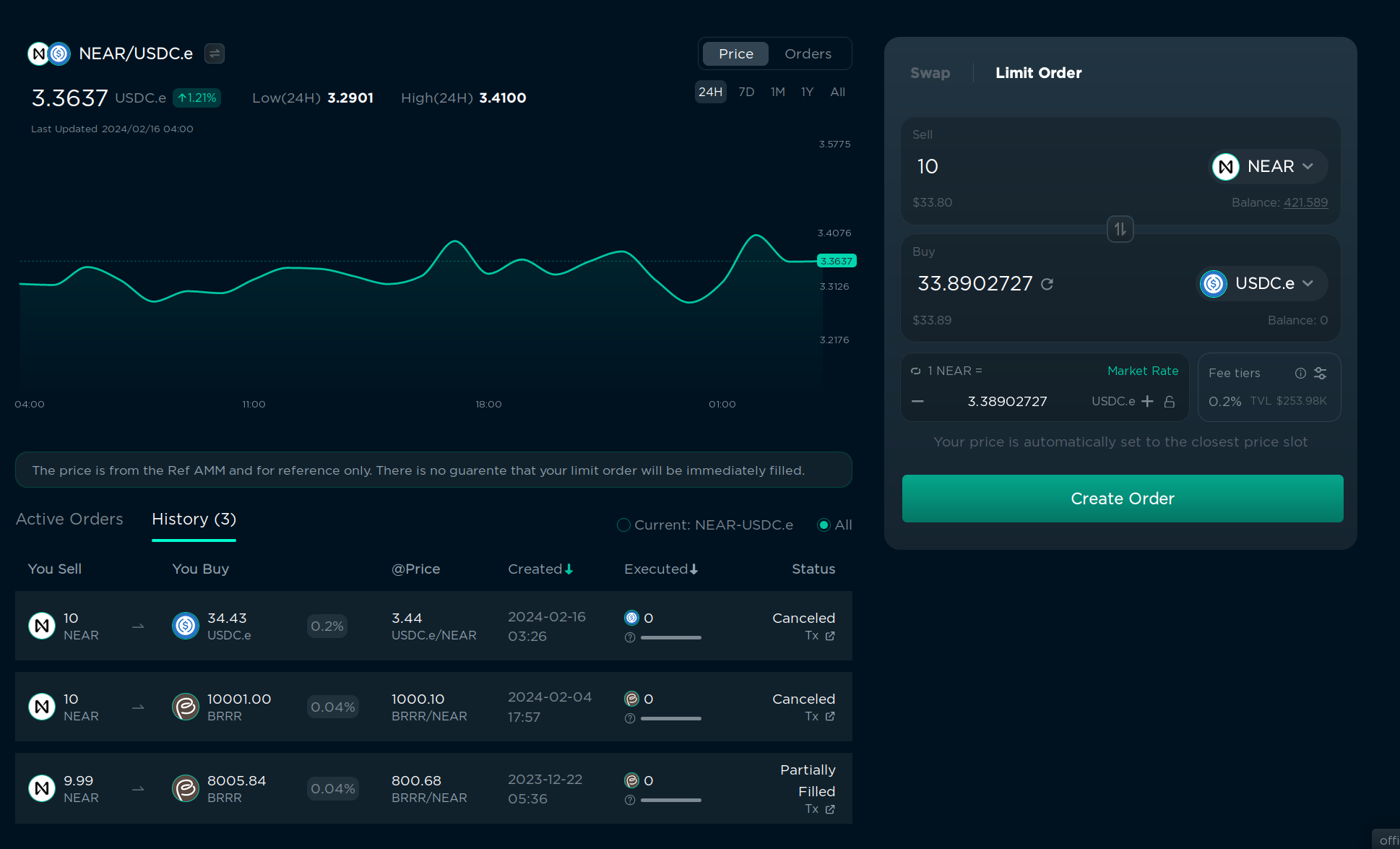
You can see a chart and order history on the left, but let’s focus on the right side.
- In “Sell” you specify the tokens to buy/sell and the amount you want to sell, it’s just like in the “Swap” menu, but the choice of tokens and buy/sell combinations is very limited.
- In “Buy” you can specify the token you want to buy and also the amount. The order price will be calculated automatically. Or you can set the order price in the bottom left corner and the receiving amount will be calculated automatically. You can click “Market Rate” to set the order price to the current market price, and then increase/decrease it as you want.
- In “fee tier” you can choose the fee you want to pay for the order. But usually there is only 1 active tier with all orders, and it’s selected by default, so I don’t recommend changing this.
- Click “Create Order” and confirm the transaction in your wallet. You will need to pay a storage fee of 0.1 NEAR, and the fee will not be refunded when the order is executed or canceled, so for small transactions it could better to use “Swap” instead of “Limit Order”.
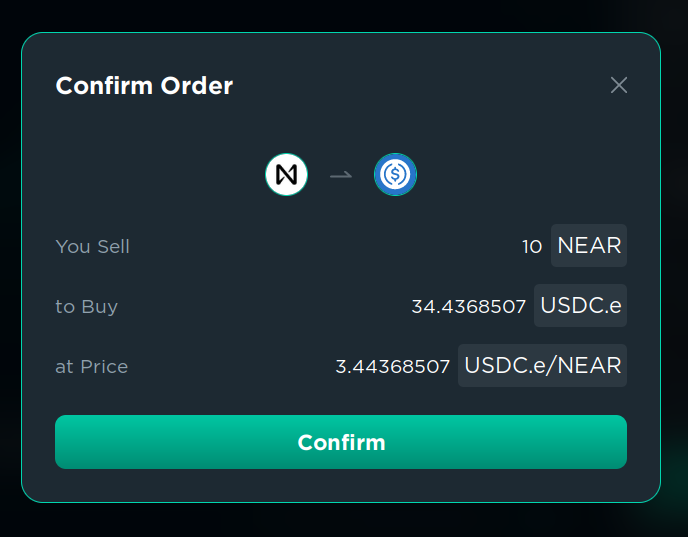
Done. Now you can wait for the price to reach the price you specified.
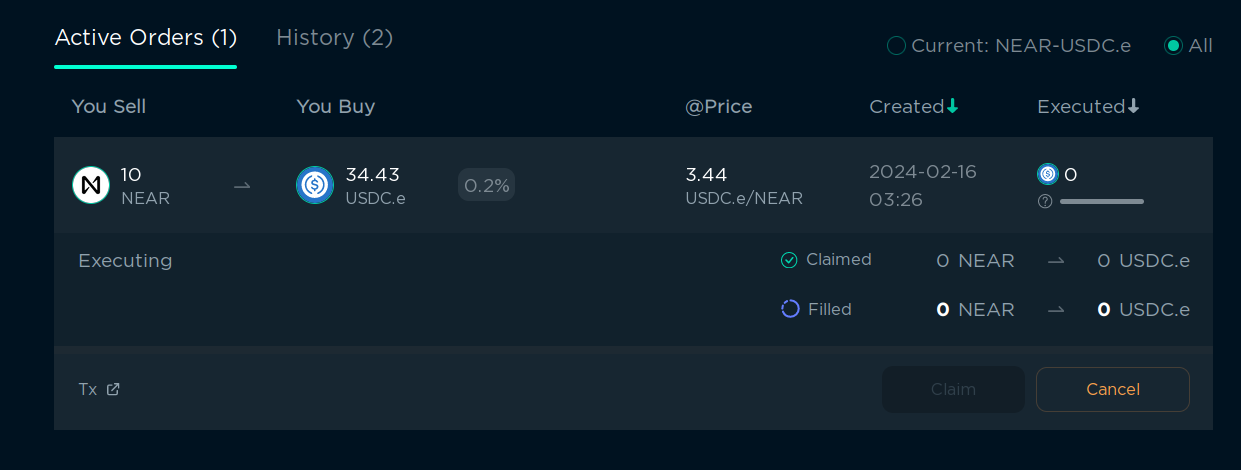
You can see your active orders in the right bottom corner. You can cancel them at any time, or claim the tokens you wanted to buy if the order was executed. It will be executed automatically when the price reaches the price you specified.
You can learn more about Ref in the official documentation
Orderly spot/perpetual trading
Orderly is a protocol that allows you to trade spot and perpetual tokens with more efficient liquidity. It’s a separate product, but the interface in hosted on ref.finance. You can find Orderly as “Orderbook” in the top left corner of the ref.finance interface:
Warning you probably don’t need to use Orderly if you’re not a professional trader. It’s more complex than ref.finance, and it’s designed for high-frequency traders. Feel free to skip this section if you’re not interested in it.
I’ll only cover the “Spot” section on this page, but they interface is quite similar on perpetual trading.
Experienced traders may find the interface familiar: It has a chart, order book, open orders, and trade history. To start trading, you have to connect your wallet and make a one-time storage deposit of 0.027 NEAR.
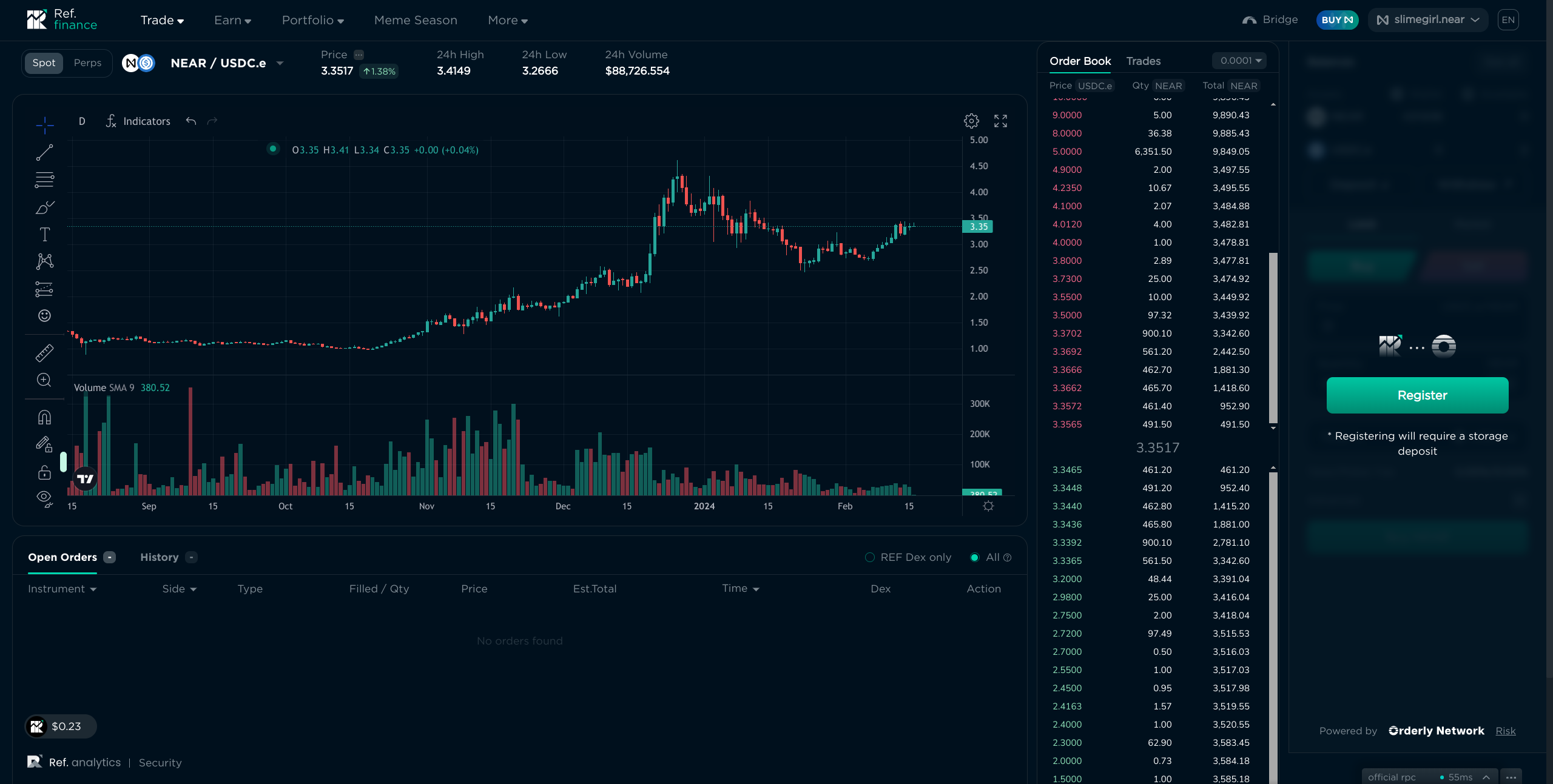
I have selected the pair NEAR/USDC.e, and in the top right corner we can see the balance of my wallet and the balance of my Orderly account. Yes, earlier I said that the money is taken from your wallet and is transferred directly into your wallet, but in Orderly the money is taken from your wallet and is transferred to your Orderly account, and then you can withdraw it to your wallet. This is done to make transactions execute faster and to reduce the fees, which can be important for high-frequency traders.
Let’s deposit some NEAR to my Orderly account. Click “Deposit”, specify the amount, and confirm the transaction in your wallet:
It may require a small (0.005 NEAR) storage deposit if it’s your first time depositing this token to your Orderly account.
Now that we have 5 NEAR in the Orderly account, we can start trading. You can see that there are 2 tabs: “Limit” and “Market”. “Limit” works the same as the limit order in the ref.finance swap menu, and “Market” works the same as “Swap”. Limit has a few advanced options:
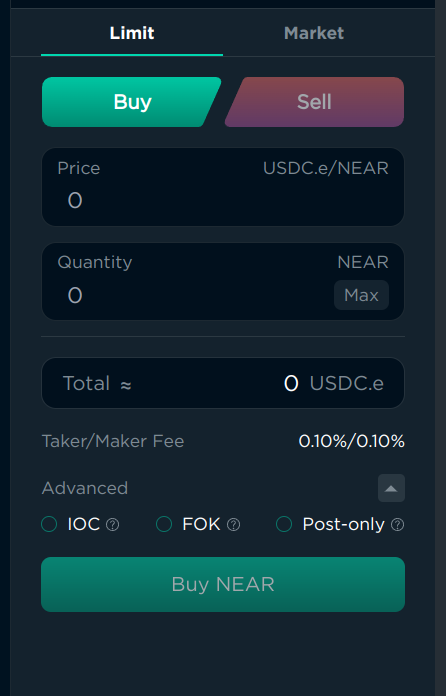
- “IOC” (Immediate or Cancel) will either execute the order immediately, or cancel it if it can’t be executed immediately, if you don’t want to wait for the price to change. It can be useful if you want to “Swap” but set the “Minimum received” manually. But I understand that it could be too hard, so I recommend using “Swap” or “Market” instead if you’re a beginner.
- “FOK” (Fill or Kill) is similar to “IOC”, but it will also not execute the order partially. This is also an advanced feature, and I recommend using “Swap” or “Market” instead if you’re a beginner. If you’re not a beginner, you probably already know what these options are used for, as they exist on all exchanges for professional traders.
- “Post Only” will only execute the order after it was added to the order book, and cancel if it would execute immediately. This is useful if the fees are lower for “maker” orders than for “taker” orders, but on spot trading the fees are the same, so it’s almost useless, here, but useful on perpetual trading.
Fees
You can see the fees under “Total”, and they are separated into “Maker” and “Taker” fees. You are a “Maker” if you add an order to the order book using “Limit” order that is not executed immediately, and you are a “Taker” if you use “Market” order or “Limit” order that is executed immediately. In our case, for NEAR/USDC.e at the time of writing it’s 0.1% for both.
You pay this fee when you buy or sell tokens, and the other person also pays this fee, so when you buy and sell $10, you pay $0.02 and other traders also pay $0.02.
Order book
When you add an order, it’s checked against the order book, and if the price can be matched with an existing order, the transaction will be executed immediately. If not, your order will be added to the order book, and it will be executed when someone else adds an order that matches your price. You can see the order book in the middle of the interface, and you can see the price, amount, and total amount of the orders for the specific prices.

When you add a “Market” order, it will always match with the best price available in the order book.
Chart
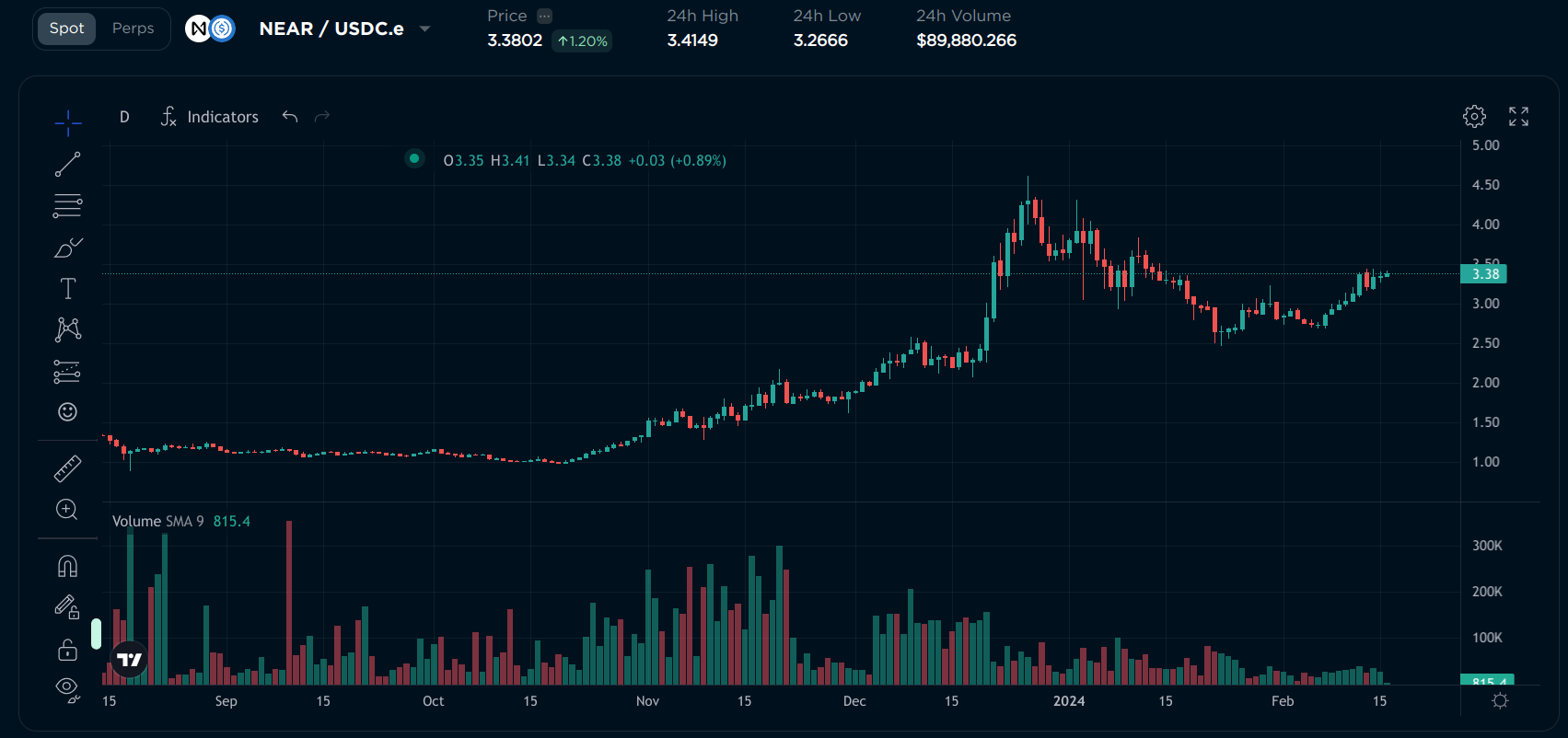
I won’t teach you how to read candlestick charts or use TradingView, there are a lot of tutorials on the internet about it. But above the chart, there are some useful statistics:
- Price: The current price of the token
- 24h High: The highest price of the token in the last 24 hours
- 24h Low: The lowest price of the token in the last 24 hours
- 24h Volume: The total amount of this token traded on Orderly in the last 24 hours. High volume means that the token is popular and the prices are more stable, while low volume means that the token is not popular and the prices can differ from other exchanges.
Opening orders
When you add a “Market” order, it will be executed immediately. When you add a “Limit” order, it will be added to the order book, and you can see your active orders below the chart. You can modify the order quantity and price by clicking the number (I know it doesn’t look clickable, but it actually is). You can also cancel the order by clicking the “Cancel” button on the right.
Withdrawal
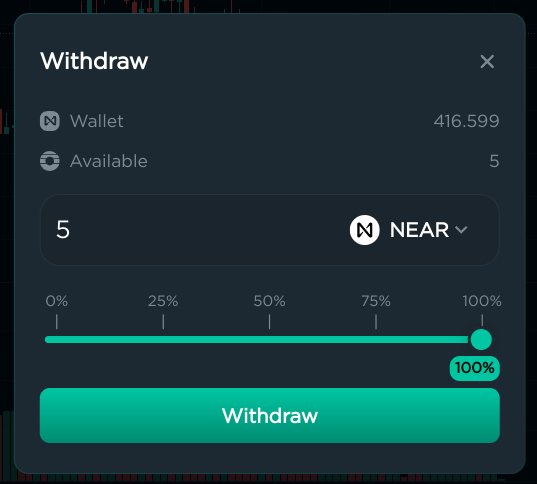
When you’re done trading, you can withdraw your tokens to your wallet. Click “Withdraw” in the top right corner, specify the amount, and confirm the transaction in your wallet.
Buying crypto with fiat
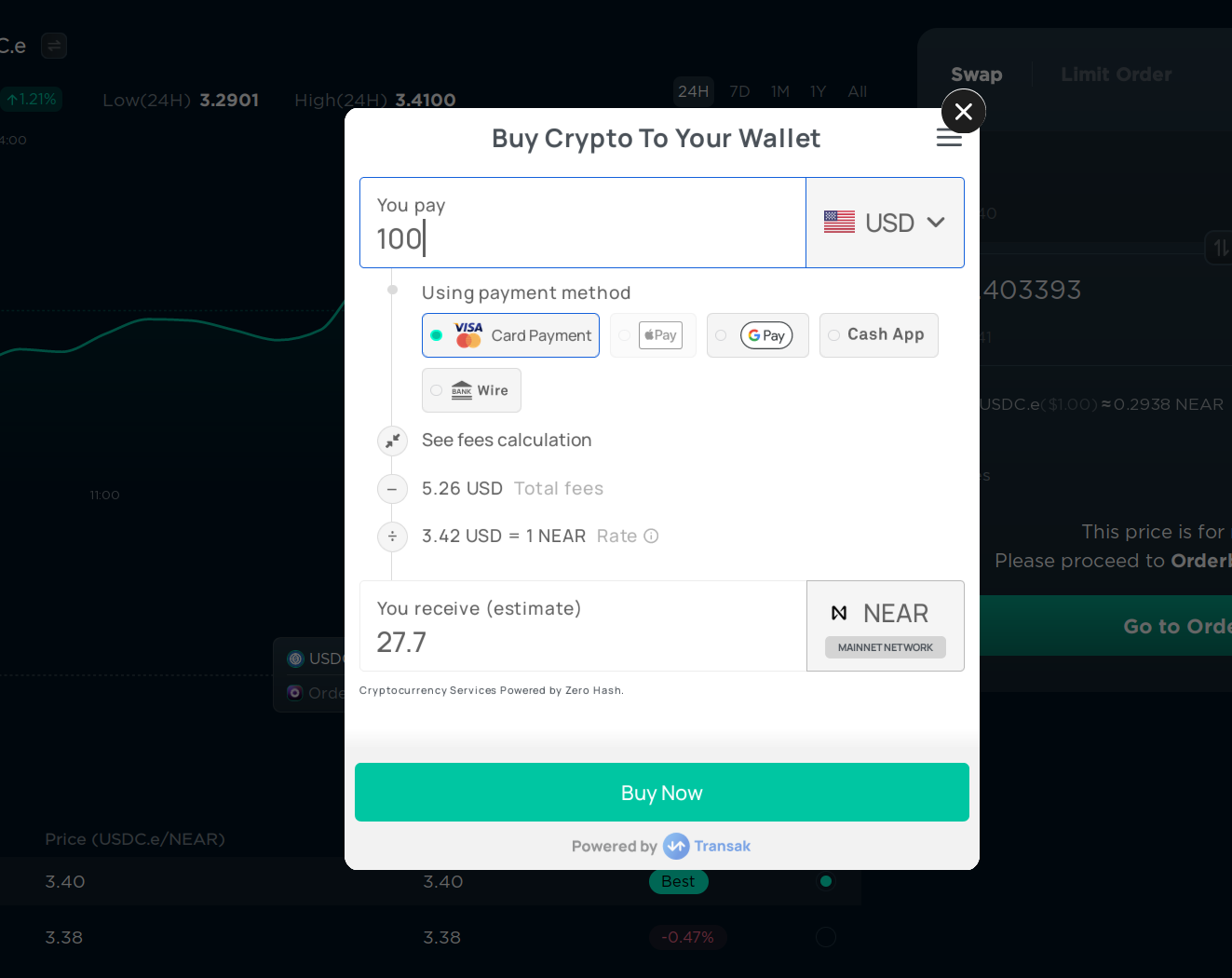
If you have USD or EUR or any other fiat currency, you can buy cryptocurrencies with it on ref.finance using the “Buy” button in the top right corner. This is done using Transak, a third-party service that allows you to buy cryptocurrencies with fiat. It’s not available in all countries, and the fees are usually higher than on exchanges, but it’s one of the easiest ways to buy cryptocurrencies with fiat without leaving ref.finance. Currently, only NEAR can be bought with fiat, but you can always swap NEAR for any other token.
CEX
CEX (centralized exchanges) are exchanges that are owned by a company, and they have control over your tokens. They are usually faster and have more features than DEXes, but they are also less secure and you have to trust the company that owns the exchange.
Here’s the difference between DEXes and CEXes:
| Feature | DEX | CEX |
|---|---|---|
| Registration | Connect your wallet | You need to create an account on the exchange, deposit money, and then you can swap tokens from your account on the exchange. Usually exchanges also require you to verify an email, set up 2-factor authentication, complete KYC (upload your ID or other government-issued document + record a video of your face), and sometimes even wait for a few days for the verification to be completed. Some territories may be banned from using the exchange. |
| Ownership | When you swap, the money is taken from your wallet and is transferred directly into your wallet | The money is taken from your wallet and is transferred to your account on the exchange, and then you can withdraw it to your wallet |
| Speed of exchange | Usually 3-5 seconds | Usually 1 second |
| Speed of deposit and withdrawal | Doesn’t need a deposit or withdrawal | Usually less than 1 hour |
| Fees | Usually 0.3% for 1 exchange (but can be changed for each token) | Usually around 0.1% for an exchange, and around $1 for withdrawal |
| Security risks | Can be hacked, but if you’re only exchanging tokens there, your money is in your wallet, so it probably won’t affect you much. There are security guarantees that the DEX’s creator or developers can’t access your funds | Can be hacked, and if all your money is in the exchange, it can be lost. Also, you have to trust the exchange to not block your account or to not steal your money (which happens quite often, even with the biggest exchanges) |
| Tokens available | Anyone can add their tokens to a DEX, so a lot of NEAR-based tokens are available. But you need to be careful, because some tokens can be scams or have a very low liquidity. | Usually only the most popular tokens are available, because the exchange checks if the project is legit. But it doesn’t mean that the token is good, it just means that the project has money to pay for the listing and is not an outright scam. CEXes support tokens from multiple blockchains, not just NEAR |
| Ease of use | Specify an amount and the token you want. But DEXes usually lack advanced trader tooling | Usually CEXes have more advanced features. Could be hard to use for beginners who never traded anything, but experienced traders in other markets will find the interface familiar |
| Fiat currencies | Usually not available, some DEXes may have a partner that allows you to buy tokens with fiat, but usually the rate is not the best. | Usually available, you can buy or sell your cryptocurrencies for your national currency |
OTC
OTC (over-the-counter) is a way to buy or sell tokens directly from another person, without using an exchange. It’s useful if you want to buy a lot of tokens at once without changing the price, or if you want to buy a token that is not available on any exchange (for example, directly from the founder before listing). When you use OTC, you have to trust the person you’re trading with, or use a trusted third party to hold the tokens until the transaction is completed, which usually costs a fee. It’s slower and less secure than using a DEX or CEX, so it’s used very rarely.